Java bank - Requirements Analysis
The first step in developing a program is to share a clear understanding of what program to make. This step is called Requirements Analysis. Requirements Analysis involves writing a scenario.
Scenario
A bank registers an account.
A bank searches for an account by account number.
A bank can find an account by the owner's name.
A bank can view a list of all accounts.
An account consists of the owner's name, account number, and balance.
An account has deposit and withdrawal functions and a balance check function. Whenever there is a change in balance, An account stores it in a transaction. A transaction consists of the transaction date, transaction time, deposit/withdrawal, transaction amount, and balance.
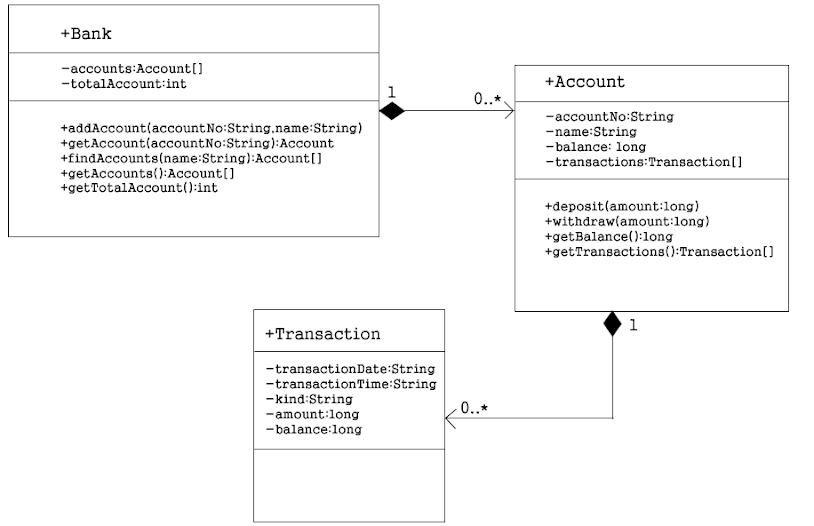
Class Diagram
You need to extract the classes, fields, and methods from a scenario.
Nouns become classes or variables. Verbs become methods.
Besides Class diagrams, there are Use case diagrams and Sequence diagrams. Depending on your project, you may need more of these, but a Class diagram is sufficient for the Java bank project.
The private is represented as -, public as +, and protected as # in a class diagram.
Class diagrams express the structure of classes and the relationships between objects.
A line connecting two classes indicates that the objects created from each class have a relationship.
A "has a" relationship is one in which an object has other objects as parts. A line with a diamond at one end indicates a "has a" relationship between objects. --The class adjacent to the diamond is the body, and the class opposite the diamond is the part--
There are two types of "has a" relationships: Composition and Aggregation.
The composition has a high degree of coupling. In a high degree of coupling, parts disappear as the body disappears. A class diagram expresses it with a diamond filled.
The aggregation has a low degree of coupling. In a low degree of coupling, the parts do not disappear even if the body disappears. A class diagram expresses it by a hollow diamond.
The number above the line indicates the maximum number of instances between related instances. 0 or * means zero or more.
An arrow is a direction in which an object calls the methods of another one.
Because a bank has multiple accounts, Bank and Account objects have a "has a" relationship.
In Java, you can implement Composition and Aggregation by declaring variables that store the part objects' references in the body object.